Mastering Diabetes: Unveiling Symptoms, Risks, and Management for Better Health
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how your body processes glucose, a vital energy source. With millions affected worldwide, understanding the symptoms, risk factors, and management strategies is crucial to living a healthier, more fulfilling life.
Symptoms of Diabetes
The symptoms of diabetes often vary between individuals and the type of diabetes. Common symptoms include:
- Frequent urination (polyuria).
- Increased thirst (polydipsia).
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Fatigue and irritability.
- Blurred vision.
Type 1 diabetes symptoms often appear suddenly, while Type 2 diabetes symptoms develop more gradually, sometimes going unnoticed for years.
Risk Factors
The risk factors for diabetes depend on the type:
1. Type 1 Diabetes: Genetic predisposition and exposure to certain viruses are primary risk factors.
2. Type 2 Diabetes: Obesity, sedentary lifestyle, family history, and age over 45 increase the risk.
3. Gestational Diabetes: Affects pregnant women with a history of obesity or prior gestational diabetes.
Management Strategies
Managing diabetes involves a combination of lifestyle adjustments, medical treatments, and regular monitoring. Here’s how:
1. Healthy Diet: Focus on whole grains, lean proteins, vegetables, and healthy fats. Limit sugar and refined carbs.
2. Regular Exercise: Physical activity improves insulin sensitivity and helps manage blood sugar levels.
3. Medications and Insulin Therapy: Insulin and oral medications, like Metformin, can be essential.
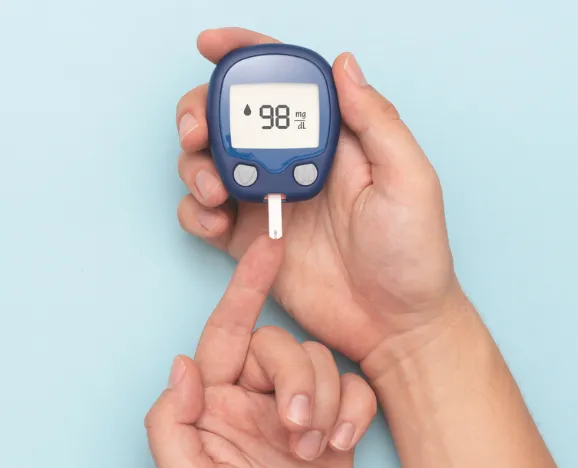
4. Monitoring Blood Glucose: Regular monitoring helps identify trends and manage levels effectively.
5. Stress Management: Techniques such as mindfulness and yoga can help prevent blood sugar spikes.
Recommended Resources
Here are some reputable companies and websites offering comprehensive diabetes information and support:
1. American Diabetes Association (ADA) – https://www.diabetes.org
2. Mayo Clinic (Diabetes Care) – https://www.mayoclinic.org
3. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) – https://www.niddk.nih.gov
4. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Diabetes Program – https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes
5. Diabetes UK – https://www.diabetes.org.uk
6. Beyond Type 1 – https://beyondtype1.org
7. International Diabetes Federation (IDF) – https://idf.org
8. Joslin Diabetes Center – https://www.joslin.org
9. WebMD (Diabetes Resources) – https://www.webmd.com/diabetes
10. Healthline (Diabetes Information) – https://www.healthline.com/health/diabetes
HTML Table:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
table {
width: 100%;
border-collapse: collapse;
}
th {
background-color: #f9f9f9;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
text-align: left;
padding: 8px;
}
td {
border: 1px solid #ddd;
padding: 8px;
}
tr:nth-child(even) {
background-color: #f2f2f2;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<table>
<tr>
<th>Aspect</th>
<th>Type 1 Diabetes</th>
<th>Type 2 Diabetes</th>
<th>Gestational Diabetes</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Causes</td>
<td>Autoimmune, genetic, environmental factors</td>
<td>Insulin resistance, obesity, lifestyle factors</td>
<td>Hormonal changes during pregnancy</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Symptoms</td>
<td>Sudden and severe</td>
<td>Gradual and often unnoticed</td>
<td>Temporary, during pregnancy</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Management</td>
<td>Insulin therapy, healthy diet</td>
<td>Diet, exercise, medications</td>
<td>Blood sugar monitoring, dietary changes</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Risk Factors</td>
<td>Family history, viral infections</td>
<td>Obesity, inactivity, age</td>
<td>History of gestational diabetes, obesity</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Long-term Risks</td>
<td>Heart disease, kidney damage</td>
<td>Stroke, neuropathy</td>
<td>Increased future risk of Type 2 diabetes</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>