Recognizing the Symptoms of Carbon Monoxide Poisoning and How to Stay Safe
Carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning is a serious and often silent health threat. Because CO is a colorless, odorless gas, it is difficult to detect without specialized equipment. When inhaled, it interferes with the body's ability to carry oxygen, which can lead to symptoms ranging from mild discomfort to life-threatening conditions. Early recognition of CO poisoning is crucial for preventing severe outcomes and ensuring safety. Here's an overview of the indicators and manifestations of CO poisoning and how to stay safe.
What is Carbon Monoxide Poisoning?
Carbon monoxide is a byproduct of burning fuels such as gas, oil, wood, or coal. Common household sources of CO include gas stoves, water heaters, furnaces, and vehicles. When these appliances are not properly ventilated or maintained, CO can build up in indoor spaces, leading to poisoning.
Common Symptoms of Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
The symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning can vary based on the level of exposure and duration. They often mimic common illnesses like the flu or food poisoning, making it hard to immediately identify. However, there are key indicators to look out for:
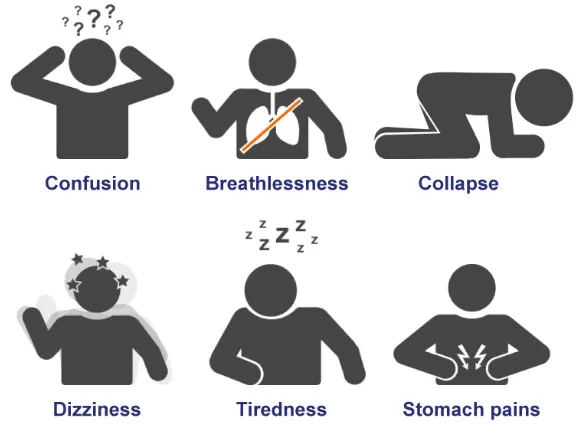
1 Headaches One of the earliest signs of CO poisoning is a headache, often described as dull and persistent. This is due to the lack of oxygen being delivered to the brain.
2 Dizziness and Confusion As CO poisoning progresses, dizziness and confusion are common. This happens because the brain is being deprived of sufficient oxygen, leading to cognitive issues and lack of coordination.
3 Nausea and Vomiting Nausea, vomiting, and stomach pain can accompany CO poisoning, as the body tries to rid itself of the harmful gas. These symptoms are often confused with food poisoning.
4 Shortness of Breath and Chest Pain Difficulty breathing and chest pain are severe symptoms of CO poisoning. When the body struggles to deliver oxygen to organs and tissues, it can cause a sensation of tightness in the chest or an increased heart rate.
5 Fatigue and Weakness Victims of CO poisoning often feel extreme fatigue and weakness because their body is unable to function properly without sufficient oxygen.
6 Loss of Consciousness In severe cases, prolonged exposure to carbon monoxide can lead to unconsciousness or even death. This is the result of the body's organs and systems shutting down due to lack of oxygen.
How to Prevent CO Poisoning
1 Install Carbon Monoxide Detectors Carbon monoxide detectors are essential for detecting dangerous levels of CO in your home. Place them in every bedroom, hallway, and near fuel-burning appliances.
2 Regular Maintenance of Appliances Ensure that all fuel-burning appliances, including stoves, heaters, and fireplaces, are regularly inspected and maintained. This will prevent CO from leaking into your home.
3 Proper Ventilation Make sure that vents and chimneys are clear and functioning properly to allow CO to escape. Never block vents or run gas-powered appliances in closed spaces like garages.
4 Avoid Idling Cars in Garages Never leave a car running in an enclosed space, such as a garage, even if the garage door is open. Carbon monoxide can quickly accumulate and be dangerous, even in small amounts.
5 Know the Symptoms and Act Quickly If you or anyone in your home shows signs of CO poisoning, immediately exit the building and seek fresh air. Call emergency services right away. Time is critical when dealing with CO poisoning.
Comparison Table: Carbon Monoxide Poisoning Symptoms
<table style="width:100%; border: 1px solid #ddd;">
<tr style="background-color: #f2f2f2;">
<th>Symptom</th>
<th>Description</th>
<th>Severity</th>
<th>Action</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Headaches</td>
<td>Persistent, dull headaches caused by reduced oxygen flow to the brain.</td>
<td>Early sign, mild to moderate severity.</td>
<td>If symptoms persist, move to fresh air and seek medical attention.</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Dizziness and Confusion</td>
<td>Feeling lightheaded and confused due to lack of oxygen.</td>
<td>Moderate to severe. May impair judgment.</td>
<td>Get fresh air immediately and avoid exertion.</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Nausea and Vomiting</td>
<td>Stomach discomfort due to the body’s response to CO exposure.</td>
<td>Mild to moderate severity.</td>
<td>Move to fresh air and hydrate, seek medical advice if symptoms worsen.</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Shortness of Breath and Chest Pain</td>
<td>Difficulty breathing and discomfort due to reduced oxygen in the blood.</td>
<td>Severe, may indicate life-threatening poisoning.</td>
<td>Seek immediate medical attention. Do not wait for symptoms to worsen.</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Fatigue and Weakness</td>
<td>Extreme tiredness caused by insufficient oxygen in the body.</td>
<td>Moderate to severe. May lead to loss of ability to function normally.</td>
<td>Rest in a well-ventilated area and seek medical help if symptoms don’t improve.</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Loss of Consciousness</td>
<td>Complete loss of consciousness due to prolonged CO exposure.</td>
<td>Critical, requires immediate medical intervention.</td>
<td>Call emergency services immediately and provide fresh air.</td>
</tr>
</table>
Conclusion
Carbon monoxide poisoning is a serious health risk, but it can be prevented with awareness and preparation. Recognizing the symptoms early is key to preventing long-term damage or death. By installing CO detectors, maintaining appliances, and following safety protocols, you can significantly reduce the risk of poisoning. Always stay alert to the symptoms and seek immediate medical attention if you suspect CO poisoning.
Recommended Websites and Companies:
1 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) - https://www.cdc.gov/co/
2 American Lung Association - https://www.lung.org/
3 National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) - https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/
4 U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) - https://www.epa.gov/indoor-air-quality-iaq/carbon-monoxide
5 WebMD - https://www.webmd.com/
6 Healthline - https://www.healthline.com/
7 Mayo Clinic - https://www.mayoclinic.org/
8 Consumer Product Safety Commission - https://www.cpsc.gov/
9 The American Red Cross - https://www.redcross.org/
10 National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) - https://www.nfpa.org/